
STSAT-2
Jump to: Mission Objectives, Mission Instrumentation, Mission Parameters, Additional Information
Mission Photos:
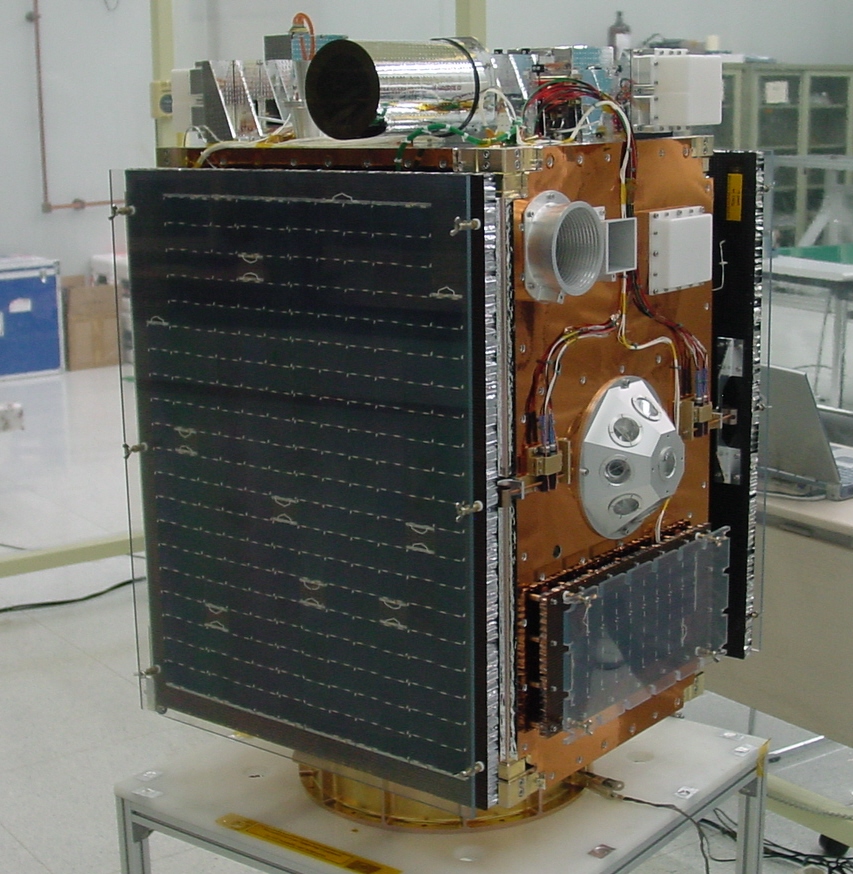

STSAT-2A and STSAT-2B
STSAT-2C
Courtesy of KAIST
Mission Objectives:
The objectives of STSAT-2 mission consist of three missions, which are the domestic development of a low earth orbit 100kg satellite which will be launched by KSLV-1(Korea Space Launch Vehicle-1) from the domestic space center (NARO Space Center),the development of advanced technology for small spacecraft, and the development and operation of world-class space science payloads. STSAT-2 have two payloads: the main payload, DREAM (Dual-channel Radiometer for Earth and Atmosphere Monitoring) and the secondary payload, LRA (Laser Retroreflector Array). The DREAM mission objectives are to acquire brightness temperature of the earth at 23.8 GHz and 37 GHz, and to acquire physical parameters such as cold liquid water and water vapor after post-processing. The mission objective of spacecraft techologies is to develop a thermally, mechanically, electrically stable and radial resistant spacecraft system having high-precision attitude determination and control capability in a high eccentric ellipsoidal orbit.
Unfortunately, the STSAT-2A satellite was lost due to a launch failure on August 25, 2009.
The launch of STSAT-2B occurred on June 10, 2010 at 08:01 GMT; the satellite was lost due to a rocket failure.
STSAT-2C satellite was successfully launched on January 30, 2013.
STSAT-2C is the third satellite to be launched by the Korea Space Launch Vehicle-1 (KSLV-1), at Naro Space Center, Korea in 2012. STSAT-2C carries five payloads. The Laser Retroreflector Array (LRA) allows the spacecraft to be tracked with centimeter accuracy by satellite laser ranging (SLR). The Langmuir probe will be used to determine the electron temperature, electron density, and electric potential of plasma. Also, the Space Radiation Effects Monitor (SREM) will be used for measurements and monitoring of the near-earth space environment. In addition, the Reaction Wheel Assembly (RWA), IR Sensor (IRS), and Femtosecond Laser Oscillator (FSO) are mounted for the new space technology verification.
For spacecraft technology experiments, STSAT-2A and STSAT-2B have the following instrumentation onboard:
- Pulsed Plasma Thruster (PPT)
- Dual-Head Star Tracker (DHST)
- Fine Digital Sun Sensor (FDSS)
- Compact on-board computer
- High-speed data transmission (10Mbps)
STSAT-2C has the following instrumentation onboard:
- Laser Retroreflector Array (LRA)
- Langmuir Probe (LP)
- Space Radiation Effects Monitor (SREM)
- Femtosecond Laser Oscillator (FSO)
- IR Sensor (IRS)
- Reaction Wheel Assembly (RWA)
Mission Parameters:
| STSAT-2A | STSAT-2B | STSAT-2C | |
| Sponsor: | Mest, KAIST | MEST, KAIST | MEST, KAIST |
| Expected Life: | |||
| Primary Applications: | Spacecraft development | Spacecraft development | Spacecraft development |
| Primary SLR Applications: | Precision orbit determination | Precision orbit determination | Precision orbit determination |
| COSPAR ID: | TBD | TBD | 1300301 |
| SIC Code: | 3801 | 3802 | 3804 |
| Satellite Catalog (NORAD) Number: | TBD | TBD | 39068 |
| Launch Date: | 10-Aug-2009 | Apr-2010 | 30-Jan-2013 |
| RRA Diameter: | 20 cm | 20 cm | |
| RRA Shape: | hemisphere | hemisphere | hemisphere |
| Reflectors: | 9 corner cubes | 9 corner cubes | 9 corner cubes |
| Orbit: | Elliptical | Elliptical | Elliptical |
| Inclination: | 80 degrees | 80 degrees | 80 degrees |
| Eccentricity: | 0.082 | 0.082 | 0.082 |
| Perigee: | 300 km | 300 km | 300 km |
| Apogee: | 1500 km | 1500 km | 1500 km |
| Weight: | 100 kg | 100 kg |
Additional Information:
Web sites:
References:
- Kim, Young-Rok; Park, Eun-Seo; Kucharski, Daniel; Hyung-Chul Lim, "Orbit Determination Using SLR Data for STSAT-2C: Short-arc Analysis", Journal of Astronomy and Space Sciences, 32(3), pp. 189-200, DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5140/JASS.2015.32.3.189




